
What was once viewed as an exception, not the norm, has quickly become normalized. 22% of Americans work remotely and 62% of American businesses employ remote workers from outside the USA. However, the challenge with this system is securing your remote workforce.
| “The security of your remote workforce depends on continuous monitoring, education, and adapting to the evolving threat landscape.” – Chris Power, CEO of Power Consulting |
Inevitably, there will be more security risks in a remote work system compared to an in-office one. However, how you roll-out your remote work program will make a big difference. You can keep your remote work secure with the right strategy.
This article will show you how. Our tips for planning the right secure remote workforce will help business owners who are planning to allow more remote work and business owners who want to improve their data security overall.
Why Move to a Remote Work System if It’s Less Secure?
Remote work has grown in popularity because many businesses see that the long-term benefits outweigh the initial security concerns. Furthermore, these security concerns are relatively easy to mitigate. Ultimately, the cost of these additional security measures is worth the long-term benefits of allowing remote work.
Here are the benefits (with most recent data):
| Increased Productivity | 90% of employees report being as or more productive working remotely compared to the office. |
| Access to More Talent | 67% of employers report that remote work has expanded their talent pool. Also, 97% of remote workers would recommend your company to others. |
| Lower Operational Costs | Companies save an average of $11,000 per year for each employee working remotely. |
| Increased Employee Retention | 54% of employees say they would change jobs for one that offers remote work. Plus, 83% of workers report higher job satisfaction after switching to remote work. |
| More Work Hours | Employees get more productive hours out of each work day. Remote workers save an average of 8.5 hours per week by not commuting. |
Source: StongDM
Factors That Influence Remote Work Security
The security challenges associated with remote work depend on the specific structure of your program. Recognizing these factors can help you implement effective policies to minimize security incidents.
1. BYOD (Bring-Your-Own-Device) Policies
Personal devices often lack the necessary updates, configurations, and monitoring of corporate-owned devices. According to CloudSecureTech, 70% of BYOD programs involve devices with limited organizational oversight, increasing risks such as outdated software and unmonitored access to company networks.
Implement Secure Single-Sign-On for your Remote Workforce
2. Program Oversight
Inconsistent enforcement of security policies across departments, teams, or locations due to decentralized IT management can create vulnerabilities. Without uniform oversight, some endpoints or systems may remain exposed, increasing overall risk.
3. Fully Remote vs. Hybrid Work
Fully remote setups present additional challenges as employees rely on various home networks and personal devices. Hybrid programs, however, provide opportunities during in-office days to update software, address security issues, and offer direct support to employees.
4. Outsourcing Foreign Workers
Managing remote teams in different countries can complicate compliance due to varying international cybersecurity standards and laws. Evaluating outsourcing locations carefully and employing US-based remote teams can simplify compliance and reduce risks.
5. Security Awareness Training
Without structured training, employees may lack the knowledge to recognize potential risks, leaving the company vulnerable to human error. Optional or insufficient training can lead to gaps in awareness, increasing the likelihood of security incidents.
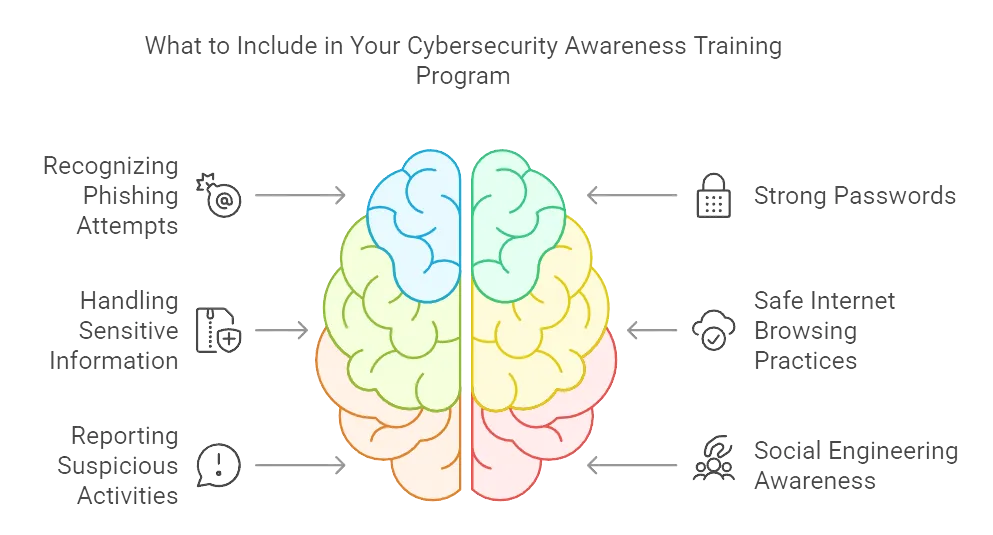
Policies That You Can Implement to Improve Your Remote Work Security
1. Secure Access Policy
Include a policy that states that employees can only access company systems through secure methods, such as virtual private networks (VPNs) or virtual desktops. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) should also be made mandatory for all logins to add an additional layer of security.
Implementation:
- Set up a company-wide VPN to encrypt traffic and provide secure remote access.
- Require MFA for all systems using software like Microsoft Authenticator or Duo Security.
- Regularly review access logs and monitor for suspicious activity.
2. Data Classification & Handling Policy
Define how remote employees should handle sensitive information, including restrictions on transferring or storing it on unauthorized devices. Also, outline encryption requirements and approved storage methods.
Implementation:
- Train employees on data classification levels and proper handling procedures.
- Require encryption for all sensitive files stored or transmitted.
- Use data loss prevention (DLP) tools to monitor and restrict unauthorized data sharing.
3. Device Security Policy
A well-defined device security policy ensures that all company devices comply with established security standards, including encryption, regular updates, and malware protection. This reduces the risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, and loss of sensitive information.
Some guidelines may vary based on device ownership, while others should remain consistent regardless of who owns the device. Here is an overview of where these guidelines generally may apply.
| Policy Description | Applies to Company-Owned Devices | Applies to Employee-Owned Devices |
| Devices must automatically lock after 5 minutes of inactivity. | ✅ | ✅ |
| IT manages and monitors all device settings, updates, and security compliance. | ✅ | ❌ |
| Employees must install approved remote management tools to ensure compliance with security policies. | ❌ | ✅ |
| Only pre-approved applications and software are permitted to be installed. | ✅ | ✅ |
| All devices must have full-disk encryption enabled to protect data in case of theft or unauthorized access. | ✅ | ✅ |
4. Wi-Fi Security Policy
Enforce that employees use secure Wi-Fi connections when accessing company resources to prevent unauthorized interception of data. Discourage employees from connecting to public Wi-Fi networks in public spaces such as airports or coffee shops.
Implementation:
- Require employees to connect only to secured networks with WPA3 or WPA2 encryption.
- Prohibit work activities on public Wi-Fi networks unless connected through a company VPN.
- Provide training on identifying safe networks and securing home routers with strong passwords and updated firmware.
5. Cloud Usage Policy
This policy governs the use of cloud-based applications and storage to prevent unauthorized access or data leaks. It also dictates how to use and what to hold in cloud storage.
Implementation:
- Restrict access to approved cloud applications for work activities.
- Use access controls and encryption for all data stored in the cloud.
- Monitor and log cloud usage to identify unauthorized activity or compliance issues.
| Learn More About Protecting Your Information Security |
6. Password Management Policy
Enforce the use of strong, unique passwords for all systems and discourage password reuse. Consider installing a secure password management system like LastPass to help employees track secure passwords across work applications.
Implementation:
- Require passwords to meet complexity standards, including length and a mix of characters.
- Mandate regular password updates and prohibit using previous passwords.
- Provide access to a company-approved password manager to store credentials securely.
7. Lost or Stolen Device Policy
Outline clear protocols for what an employee should do if their device is lost or stolen. You should also highlight what your IT professionals should do to help minimize the risk of the lost or stolen device becoming the source of a data breach.
Implementation:
- Require employees to report lost or stolen devices immediately to the IT department or a designated contact.
- Use mobile device management (MDM) software to remotely lock, locate, or wipe devices.
- Implement data encryption on all devices to protect information even if a device is compromised.
- Provide a step-by-step incident response guide for employees to follow in such situations.
| Count on NYC’s Leading IT Consultants to Enhance Your Remote Work IT Security | ||
| Brooklyn | Manhattan | Queens |
Better Secure Your Remote Workforce With Power Consulting
If you need assistance either crafting or enforcing your remote workforce security policy, you can count on Power Consulting. Our team of professionals can monitor and manage your IT networks 24/7 using CISSP security features and practices.
Reach out today to get started.



